About company
UNITES Systems a.s.
Kpt. Macha 1372
757 01 Valašské Meziříčí
Czech republic
T: +420 571 757 230
E: e-mail contacts
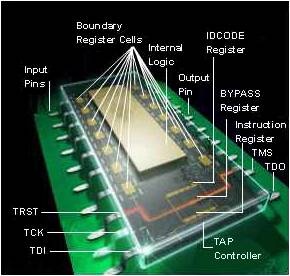
Boundary scan
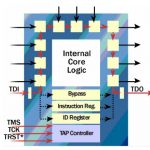
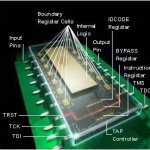
Boundary Scan, also known as JTAG (IEEE 1149.1 standard), is a method for testing digital circuits that enables access to connectors and internal signals of integrated circuits without the need for physical probe contact. Instead of direct access, it uses a chain of shift registers placed along the pins of the chip.
What is JTAG used for?
- Testing connections between components (even through passive elements such as resistors),
- In-system programming of memories (e.g., Flash),
- Diagnostics and debugging of processor cores,
- Verification of connections even without access to the internal logic of the device.
- If even a single chip on the board supports Boundary Scan, this method can be used. The more components support JTAG, the higher the possible fault coverage.
How does it work?
- Shift register cells are placed along the pins of the chip.
- Each pin can be controlled or observed independently of the core logic.
- Connections between multiple chips can be verified – for example, the output of one chip to the input of another.
- Software can generate test sequences or write data (e.g., to memory).
Advanced Applications
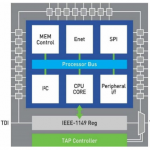
- JTAG debug logic in microprocessors allows access to the CPU core and buses for emulation testing and programming.
- CoreCommanders (e.g., from JTAG Technologies) provide direct control over processors of various architectures.
- There are also mixed-signal I/O modules that expand testing capabilities to include analog circuitry.
Advantages of Boundary Scan
- Does not require physical test points
- Suitable for miniaturized and multilayer boards
- Can be used even for small-series or prototype production
- Integration into functional testing, ICT, or FCT systems
Summary
Boundary Scan is an extremely useful tool for testing and debugging complex digital systems. It offers high fault coverage, flexibility, and cost savings – especially where physical access to circuits is limited or impossible.